library(mapa)8 Data Visualization
The mapa package provides comprehensive visualization functions to explore and present your pathway enrichment and functional module results. This chapter covers four main visualization approaches: pathway bar charts, module information plots, similarity networks, and relationship networks.
Prerequisites: Before creating visualizations, ensure you have completed the previous analysis steps. The visualization functions require objects from:
- Enrichment analysis:
enrich_pathway()ordo_gsea() - Module clustering:
merge_pathways()andmerge_modules()ormerge_pathways_bioembedsim() - Optional: LLM interpretation:
llm_interpret_module()
8.1 Overview of Visualization Functions
mapa provides four main visualization functions:
| Function | Purpose | Best Used For |
|---|---|---|
plot_pathway_bar() |
Horizontal bar charts of top enriched items | Showing enrichment strength across pathways/modules |
plot_module_info() |
Multi-panel module details (network + bar + wordcloud) | Detailed examination of specific modules |
plot_similarity_network() |
Similarity-based networks | Understanding pathway relationships and clustering |
plot_relationship_network() |
Multi-level hierarchical networks | Visualizing connections across biological levels |
8.2 Bar Chart Visualization
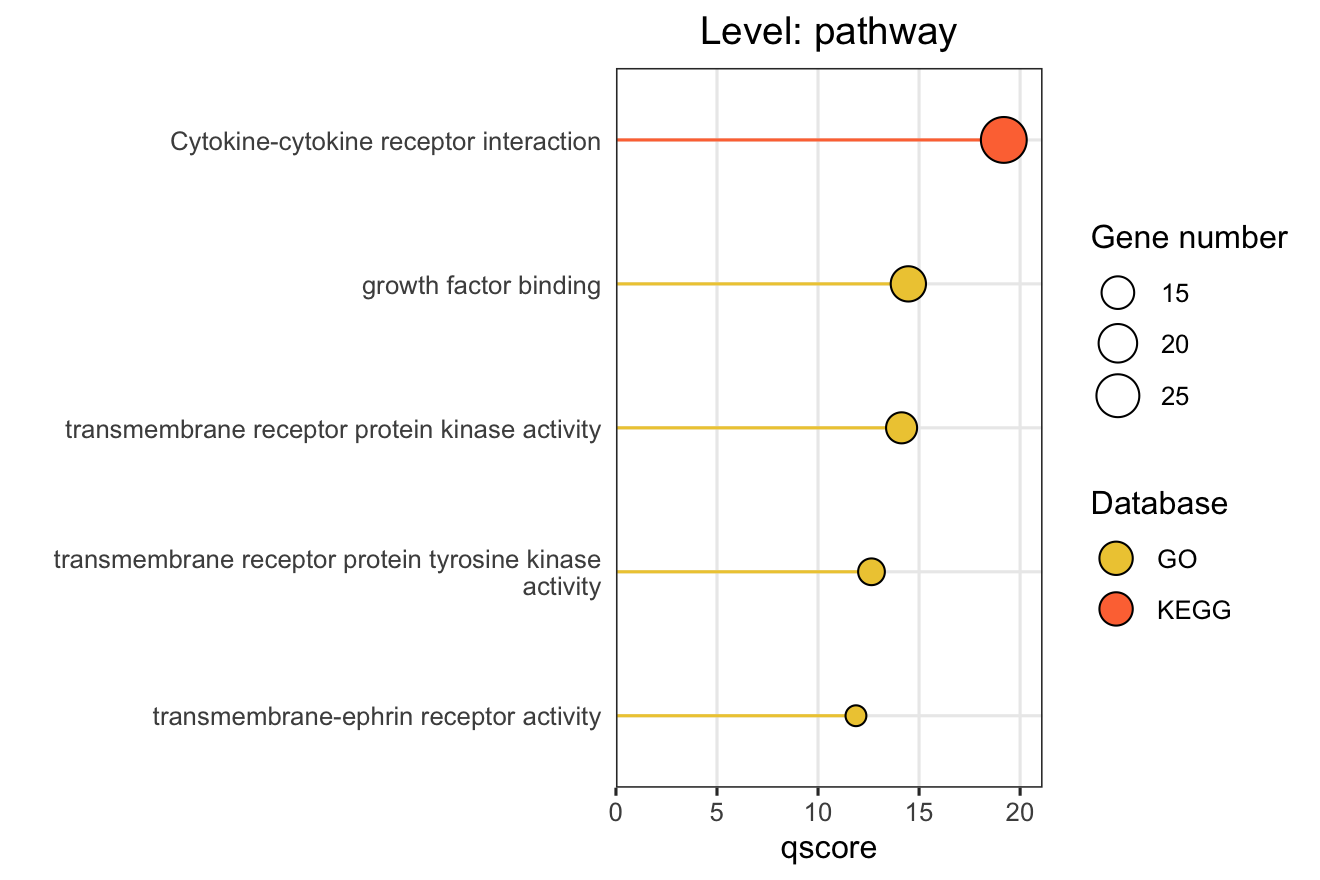
The plot_pathway_bar() function creates horizontal bar charts showing the top enriched pathways, modules, or functional modules. This is ideal for presenting enrichment results in publications.
8.2.1 Basic Usage
# Basic pathway-level bar chart
plot_pathway_bar(
object = enriched_functional_modules,
level = "pathway",
database = c("go", "kegg", "reactome"),
top_n = 5,
x_axis_name = "qscore" # "-log10(FDR)" for ORA
)
8.2.2 Key Parameters
| Parameter | Description | Options/Default |
|---|---|---|
level |
Analysis level | "pathway", "module", "functional_module" |
x_axis_name |
X-axis metric | ORA: GSEA: |
line_type |
Bar style | "straight" (default), "meteor" |
llm_text |
Use LLM names for functional modules | TRUE/FALSE |
top_n |
Number of items to show | Default: 10 |
database |
Databases to include | c("go", "kegg", "reactome", "hmdb", "metkegg") |
X-axis Metrics Explained:
- qscore: -log₁₀(adjusted p-value), higher values indicate more significant enrichment
- RichFactor: Ratio of input genes in pathway vs. all genes in pathway
- FoldEnrichment: Enrichment fold change (GeneRatio divided by BgRatio), see Section 3.3
- NES: Normalized Enrichment Score (GSEA only), positive/negative indicates up/down-regulation
8.3 Module Information Plots
The plot_module_info() function provides detailed, multi-panel visualizations of individual modules, including network topology, pathway rankings, and word clouds. The content of each plot depends on the analysis level:
| Plot level |
(Database-specific) |
(Cross-database) |
|---|---|---|
| Network | Shows pathways within the database-specific module and their similarity connections | Shows representative pathways from database-specific modules (SimCluster) or individual pathways (EmbedCluster) |
| Bar plot | Ranks individual pathways within the module by significance | Ranks the representative pathways or database-specific modules by significance |
| Word cloud | Word frequency from pathway descriptions, with word size reflecting statistical significance | Word frequency from all pathway descriptions in the functional module, with word size proportional to the sum of statistical significance values |
Word Cloud Interpretation: Word size reflects the cumulative statistical significance of pathways containing that word:
- For ORA (Over-Representation Analysis): Word size is proportional to the sum of -log10(adjusted p-value) across pathways containing that word. Larger words indicate terms appearing in pathways with stronger statistical enrichment.
- For GSEA (Gene Set Enrichment Analysis): Word size is proportional to the sum of |NES| (absolute Normalized Enrichment Score) across pathways containing that word. Larger words indicate terms appearing in pathways with stronger enrichment signals, regardless of direction (up- or down-regulation).
8.3.1 For Functional Modules
# Get available module IDs first
enriched_functional_modules@merged_module$functional_module_result$module
# Create detailed plots for a specific module
module_plots <- plot_module_info(
object = enriched_functional_modules,
level = "functional_module",
module_id = "Functional_module_42",
llm_text = FALSE # Set to TRUE to use LLM-generated names if available
)Access individual plots:
# Network of the representative pathways of database-specific modules within the functional module
module_plots$network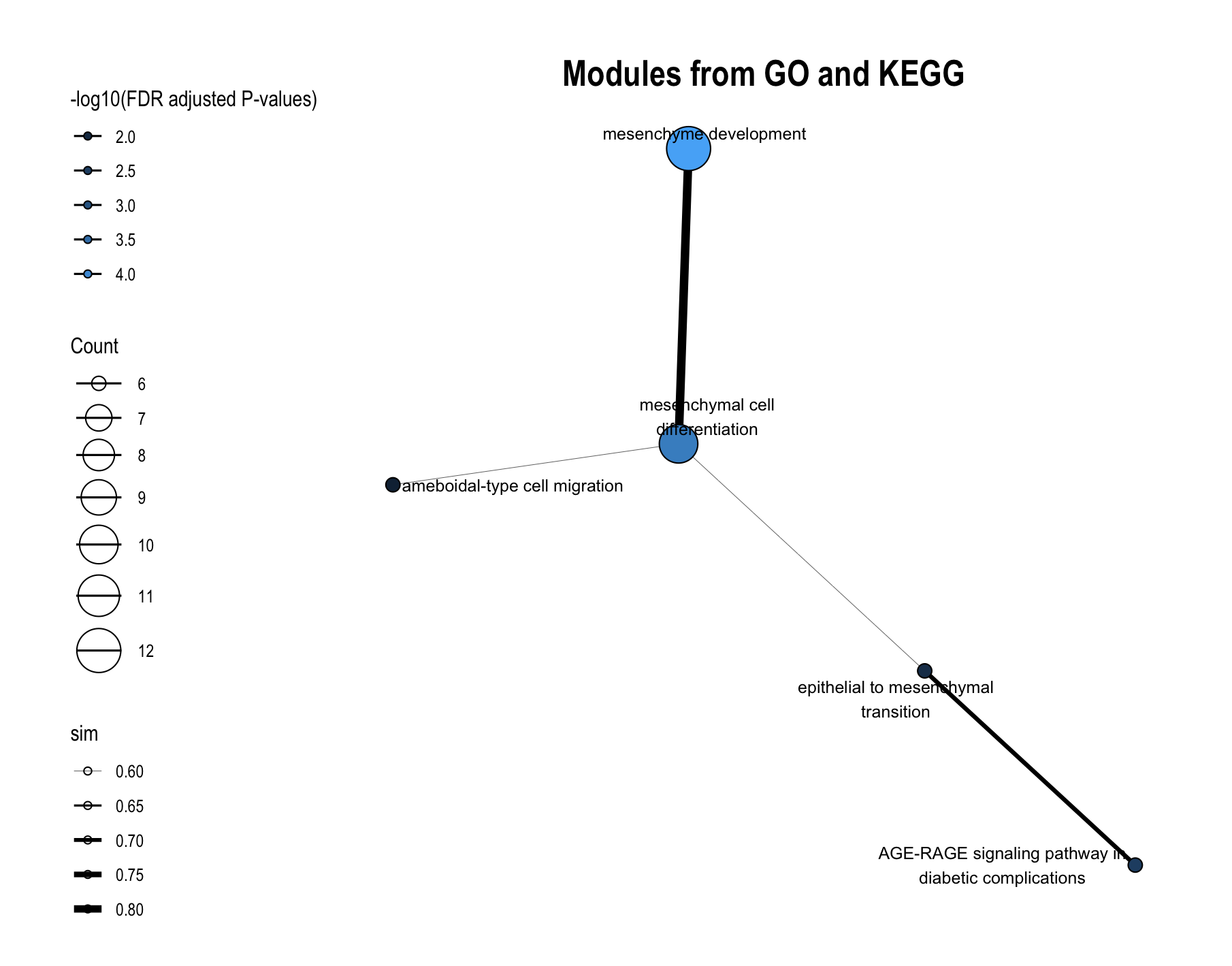
# Ranked the representative pathways of database-specific modules within the functional module by significance
module_plots$barplot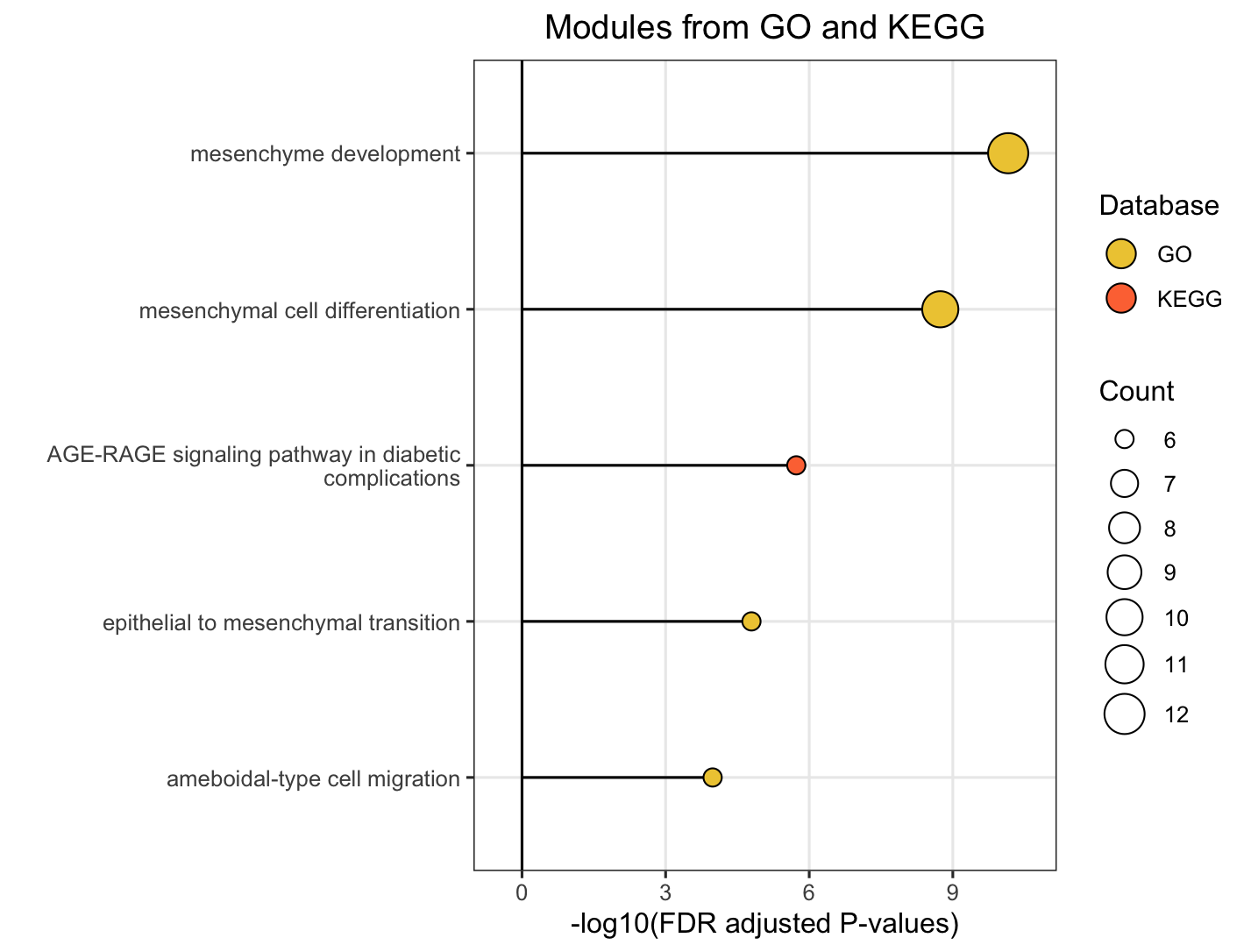
# Word cloud of pathway descriptions of the representative pathways of database-specific modules within the functional module
module_plots$wordcloud
8.3.2 For Database-Specific Modules
# Examine a specific KEGG module
go_plots <- plot_module_info(
object = enriched_functional_modules,
level = "module",
database = "go",
module_id = "go_Module_25"
)
# View the plots
go_plots$network
go_plots$barplot
go_plots$wordcloud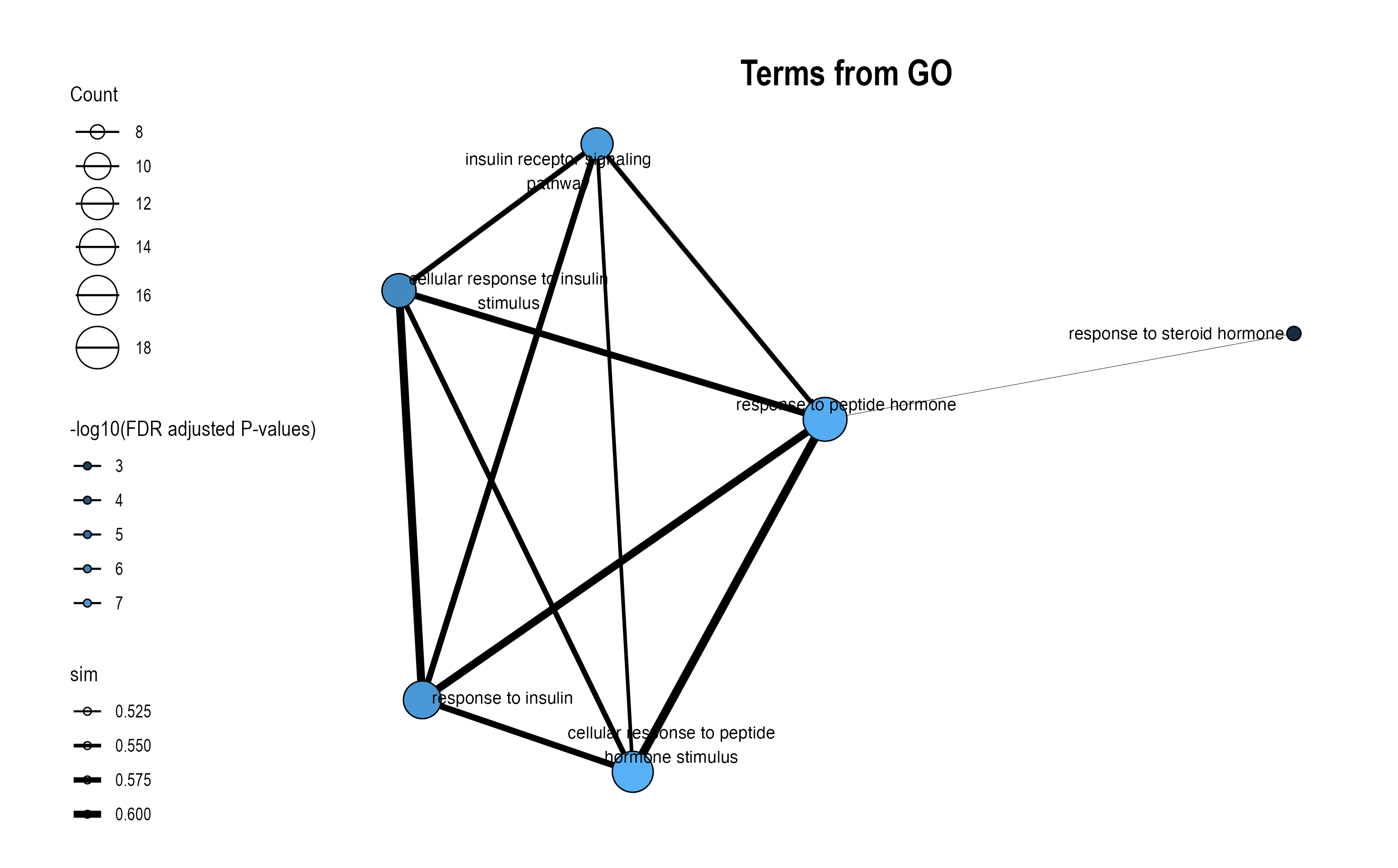
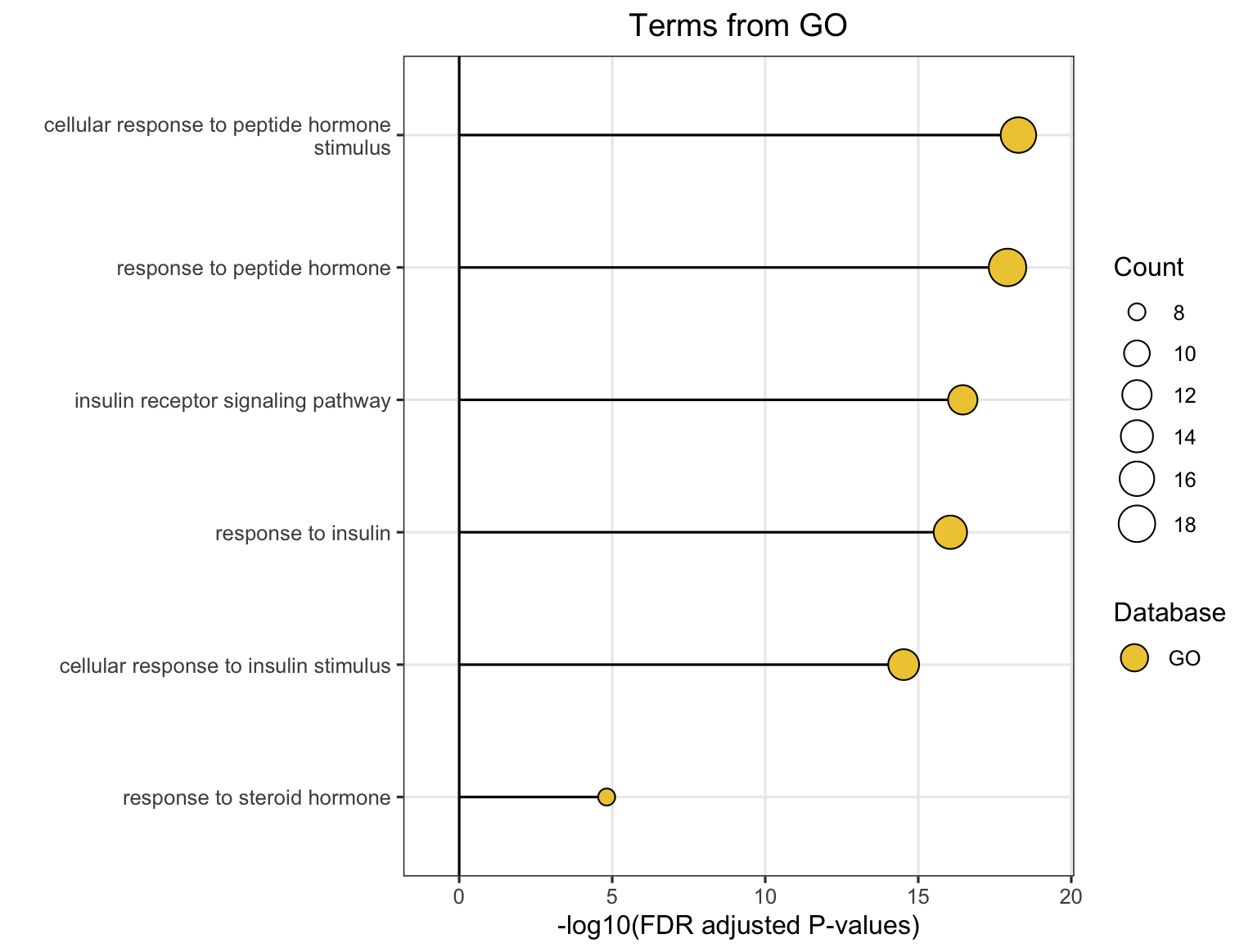

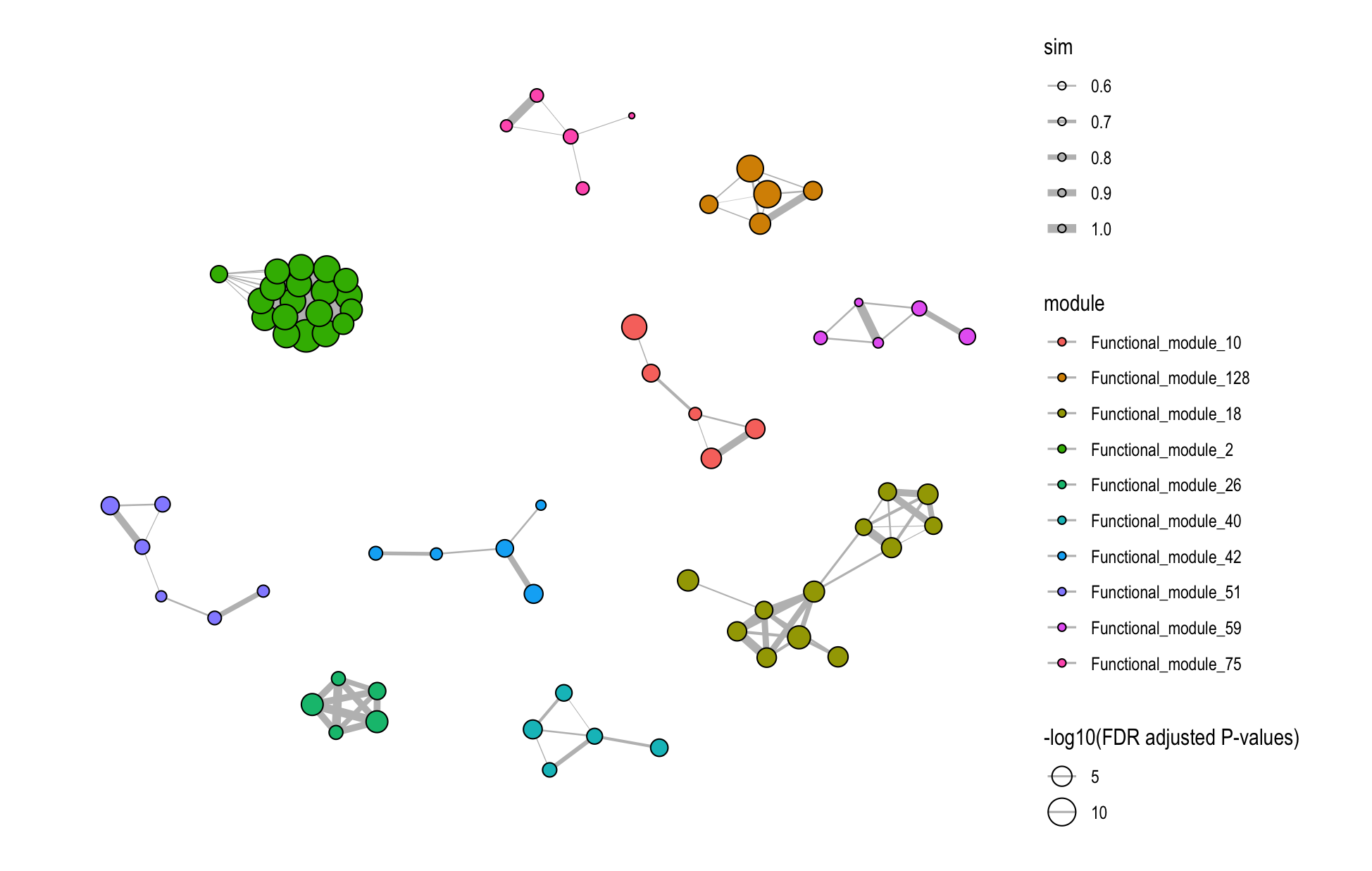
8.4 Similarity Network Visualization
The plot_similarity_network() function visualizes how pathways or modules cluster together based on similarity metrics.
8.4.1 Basic Usage
# Functional module similarity network
plot_similarity_network(
object = enriched_functional_modules,
level = "functional_module",
degree_cutoff = 4, # Only show modules with >2 pathways
text = TRUE
)
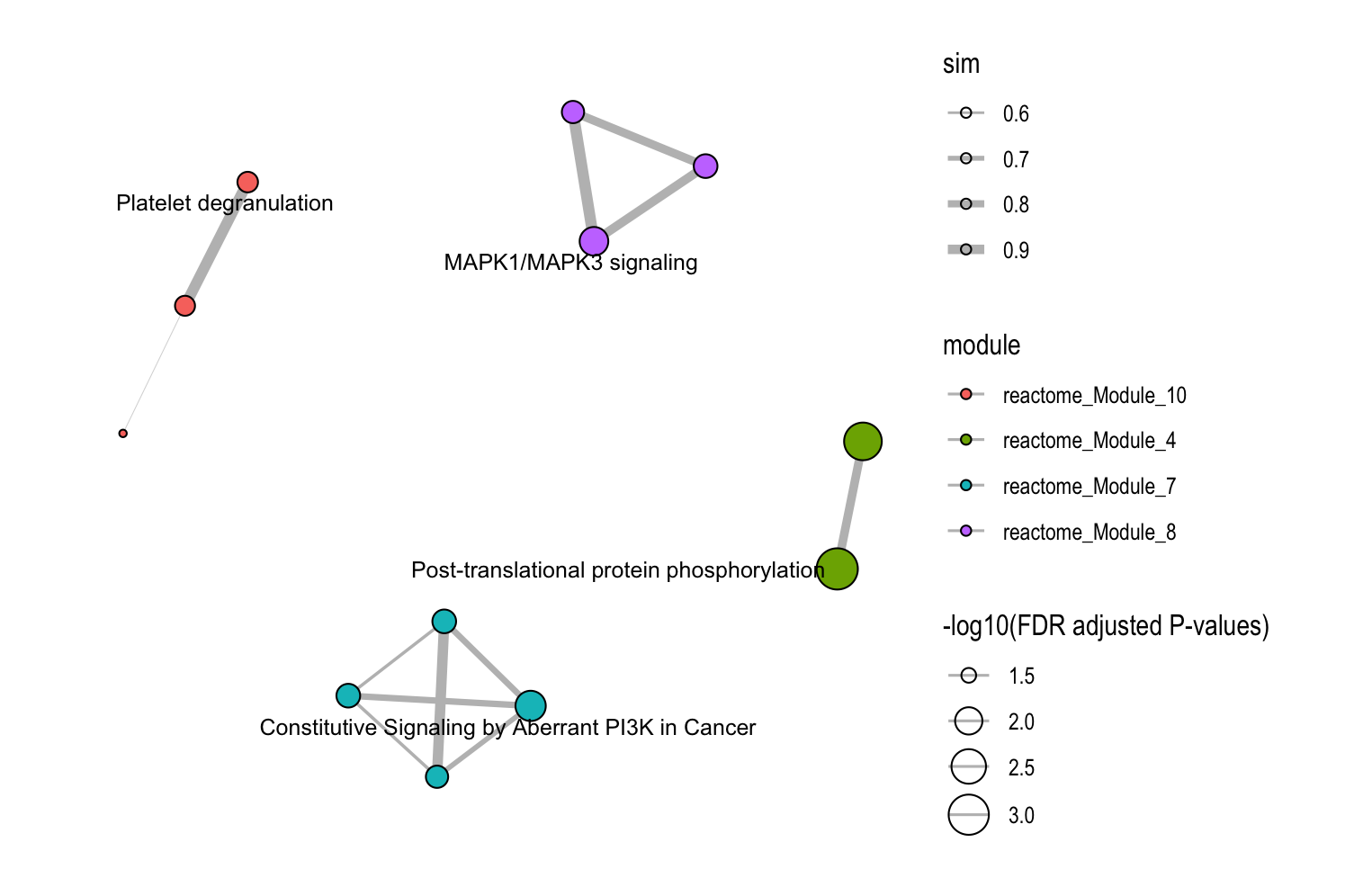
8.4.2 Database-Specific Networks
# GO module network
plot_similarity_network(
object = enriched_functional_modules,
level = "module",
database = "go",
degree_cutoff = 5,
text = TRUE
)
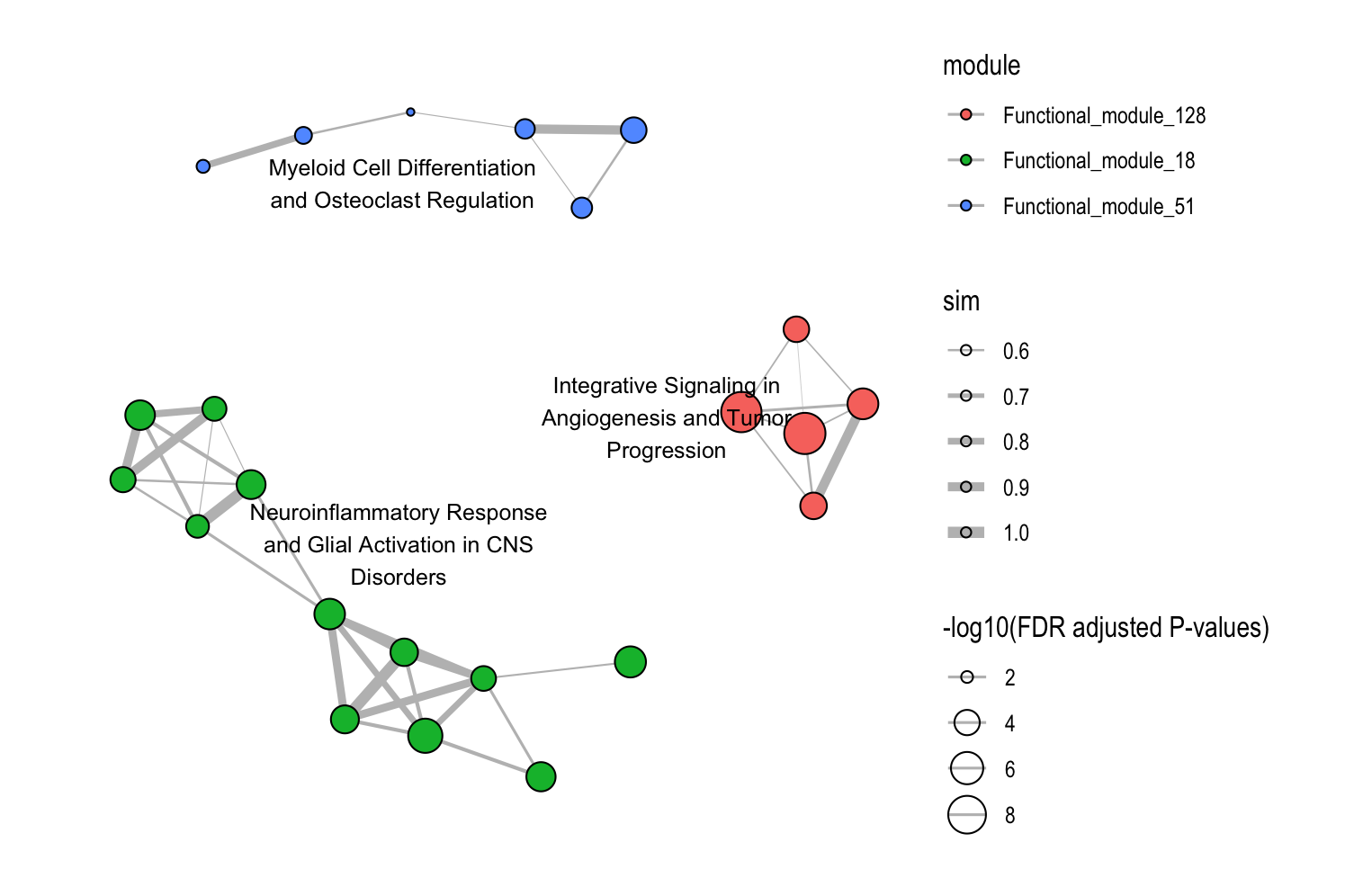
8.4.3 Focus on Specific Modules
# Examine specific modules only
plot_similarity_network(
object = llm_interpreted_modules,
level = "functional_module",
module_id = c("Functional_module_18", "Functional_module_51", "Functional_module_128"),
llm_text = TRUE
)
8.4.4 Key Parameters
| Parameter | Description | Usage |
|---|---|---|
degree_cutoff |
Minimum pathways per module | Filter small modules |
text |
Show representative names | One label per module |
text_all |
Show all pathway names | All nodes labeled |
llm_text |
Use LLM-generated names | For functional modules with LLM interpretation |
module_id |
Specific modules to show | Focus on modules of interest |
8.5 Relationship Network Visualization
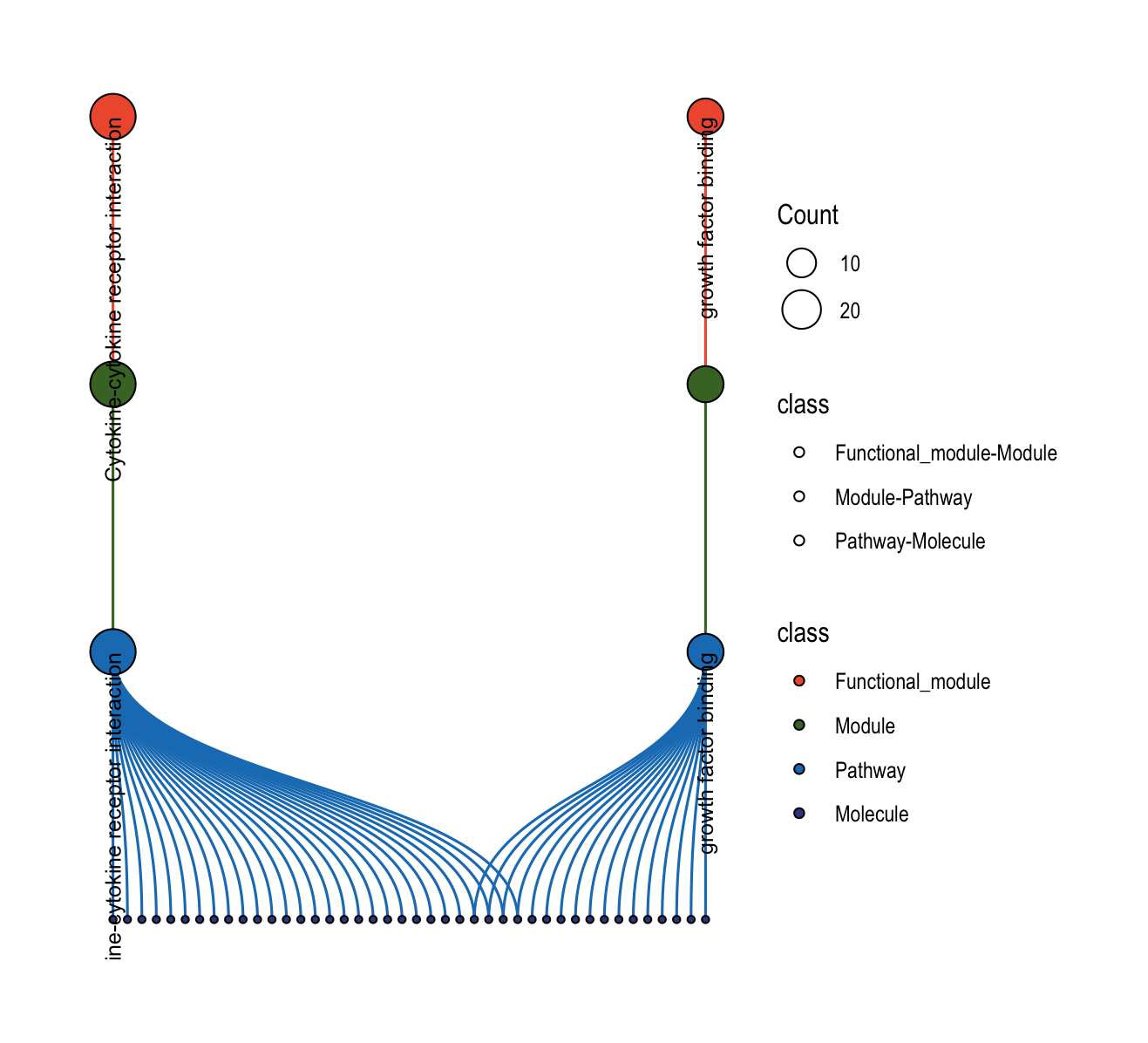
The plot_relationship_network() function creates comprehensive multi-level networks showing relationships between functional modules, modules, pathways, and molecules.
8.5.1 Basic Usage
object <- enriched_functional_modules
object@merged_module$functional_module_result <-
head(object@merged_module$functional_module_result, 2)
# Full hierarchy: functional modules → modules → pathways → molecules
plot_relationship_network(
object = object,
include_functional_modules = TRUE,
include_modules = TRUE,
include_pathways = TRUE,
include_molecules = TRUE,
functional_module_text = TRUE,
pathway_text = TRUE,
molecule_text = FALSE
)
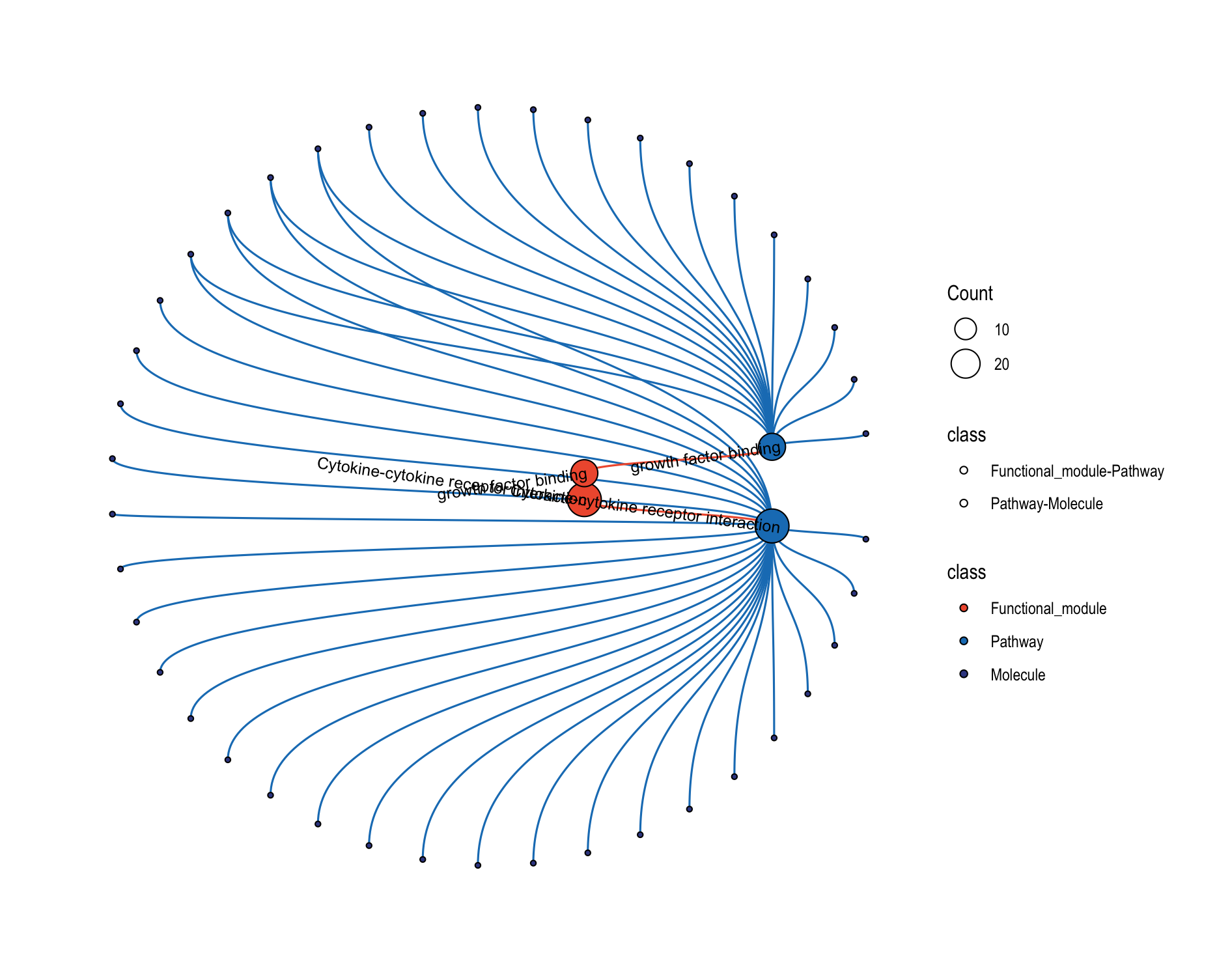
8.5.2 Circular Layout
# Circular layout for better visualization of complex networks
plot_relationship_network(
object = object,
include_functional_modules = TRUE,
include_modules = FALSE,
include_pathways = TRUE,
include_molecules = TRUE,
circular_plot = TRUE, # Concentric circles layout
functional_module_text = TRUE,
molecule_text = FALSE
)
8.5.3 Customization Options
| Parameter | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
include_* |
Include specific node types | All TRUE |
*_color |
Node colors by type | Predefined colors |
*_text |
Show text labels | Varies by type |
*_text_size |
Label font size | 3 |
circular_plot |
Circular vs. horizontal layout | FALSE |
8.6 Troubleshooting Visualization Issues
Common Issues and Solutions:
- Empty plots or warnings about no data
- Check that your cutoffs (
p.adjust.cutoff,count.cutoff) aren’t too stringent - Verify that modules exist at the specified level
- Check that your cutoffs (
- Text labels overlapping or unreadable
- Adjust
y_label_widthparameter - Use
text_all = FALSEto show only representative labels - Increase plot dimensions when saving
- Adjust
- EmbedCluster results at module level
- Use
level = "functional_module"for EmbedCluster results - EmbedCluster bypasses database-specific modules
- Use
- LLM text not appearing
- Ensure
llm_interpret_module()was run successfully - Check that the object contains LLM interpretation results
- Ensure
8.7 Next Steps
Continue to Results Report to learn how to generate comprehensive analysis reports that combine all your results into professional documents.
